Understanding the A1C Test and Why It’s So Important
The A1C test, also known as the hemoglobin A1c test, is a blood test that measures the average blood sugar level over the past 2 to 3 months. The HbA1c test, is also commonly known as the glycated hemoglobin test, is a valuable diagnostic tool used to monitor and manage diabetes. This simple blood test provides a comprehensive analysis of your average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. By measuring the levels of HbA1c in your blood, healthcare professionals can determine whether your blood sugar levels have been consistently high or low over an extended period of time. This information is crucial in developing an effective treatment plan and making necessary lifestyle changes to manage the condition.The HbA1c test is a simple blood test that provides a snapshot of your average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months, and it is commonly used to diagnose and monitor diabetes. For those living with diabetes or at risk for developing the condition, regular A1C testing is crucial for monitoring how well blood sugars are being controlled.
The A1C test measures your body’s percentage of hemoglobin proteins in red blood cells that have become glycated or coated with sugar. The more excess sugar circulating in your bloodstream, the higher this percentage will be.
Some key facts about the A1C:
- It does not require fasting and can be taken at any time of day
- Provides an average blood sugar level over 2-3 months, unlike finger prick tests, which just measure the moment
- The gold standard test for both diagnosing diabetes and monitoring glucose control
- Reduces the effects of fluctuations in blood sugar from things like meals or exercise
What Do Your A1C Levels Mean?
The A1C test results provide a percentage that correlates with your estimated average blood sugar levels:
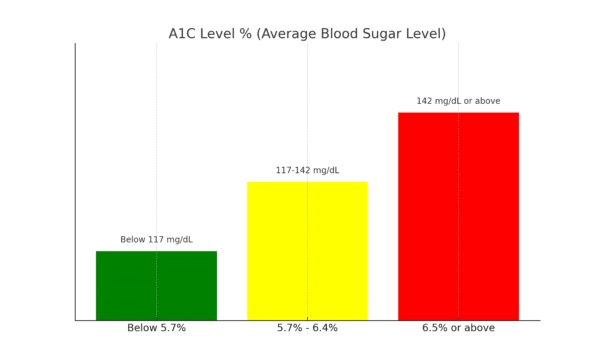
- A1C Level % (Average Blood Sugar Level)
- Below 5.7% (Below 117 mg/dL) = Normal range
- 5.7% – 6.4% (117-142 mg/dL) = Prediabetes range
- 6.5% or above (142 mg/dL or above) = Diabetes range
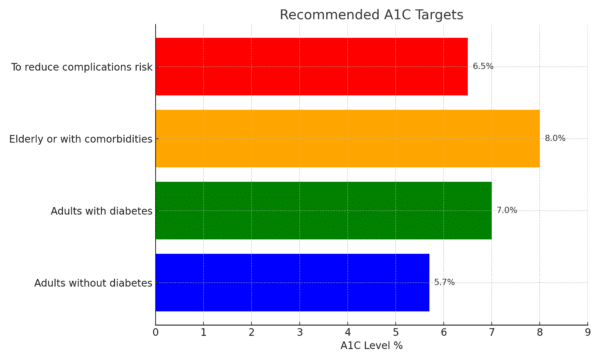
For most people without diabetes, a normal A1C level is below 5.7%. The American Diabetes Association recommends an A1C target of:
- Less than 7% for adults with diabetes
- Less than 8% for elderly or those with comorbidities
- Less than 6.5% to reduce risks of complications like eye, kidney or nerve damage
The lower your A1C, the lower your risks of developing complications from chronically high blood sugars.

How Often Does Your A1C Change and Why?
For those without diabetes who maintain relatively stable blood sugars, their A1C levels tend to remain fairly consistent over time if their diet, exercise, weight and overall health doesn’t change significantly.
For those with diabetes, A1C levels can vary much more frequently and are impacted by:
- Changes in medication dosages or timings
- Diet and exercise habits
- Weight fluctuations
- Illness or other stressors
- Hormonal shifts
In general, experts recommend:
- Testing every 3 months for those with diabetes
- Testing every 6-12 months for those without diabetes or at increased risk
The more frequently you test, the better you can identify trends and make necessary adjustments.

What Causes Large A1C Fluctuations?
While your A1C provides an overall trend, large swings between tests may indicate:
- Poor medication adherence or dosing issues
- Extended periods of very high or low blood sugars
- Recent illness or infection
- Changes in diet, activity levels or weight
- The effects of a new medication
- Presence of anemia or certain blood disorders
An A1C change of 1 percentage point (e.g. 7% to 8%) equates to an average blood sugar change of approximately 35 mg/dL. So a 0.5% increase could mean your daily average increased by almost 20 mg/dL!
Those with prediabetes can potentially see rapid A1C increases as insulin resistance progresses. While those with well-controlled diabetes may only see gradual changes over months.
Why Get Tested and Who Needs the A1C?
Beyond helping diagnose prediabetes and diabetes, the A1C test provides an invaluable glucose monitoring tool for:
People with Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes
The A1C helps identify how lifestyle changes or medication adjustments are impacting average blood sugar control. Testing every 3 months is the standard.
Those At High Risk for Developing Diabetes
By establishing a baseline A1C and monitoring its changes over time, you can take preventative measures if prediabetes develops. High risk groups like those with obesity or PCOS typically test every 6-12 months.
Women with Gestational Diabetes
The A1C helps monitor how blood sugars are being controlled throughout pregnancy to reduce risks of complications for mom and baby.
Anyone Experiencing Recurring Symptoms
Increased thirst and urination, unintentional weight loss, increased hunger, vision changes, and fatigue can all be signs of chronically high blood sugars.
Getting an A1C Test at Walk-In Lab
Many people don’t realize you can get an A1C test without a doctor’s order at Walk-In Lab. This can help you manage the cost of getting tested for diabetes.
Select the A1C or Diabetes monitoring test online, locate a lab near you, and then get your results online.
Your results are reviewed by a physician and made available in your private online account typically within 24-48 hours.
This provides an easy way to take charge of your health privately and discreetly without needing insurance or a doctor’s visit. The best part? Costs are often 50-80% less than paying out-of-pocket at a doctor’s office or hospital.

Final Thoughts: Why the A1C Test Is So Crucial
The A1C is a simple blood test, but provides amazingly powerful insights into your body’s glycemic control over the past 2-3 months.
For those living with diabetes, regular A1C testing helps:
- Identify how medication or lifestyle adjustments are working
- Catch blood sugar issues before complications arise
- Motivate you to improve nutrition and self-care habits
- Provide data to share with your diabetes care team
And for those without diabetes, getting an A1C every 6-12 months can serve as an early warning system for prediabetes or diabetes risk.
While daily finger prick glucose tests are still important, the A1C allows you to see the bigger picture of how your body is responding to diabetes treatment and management over time.
So if it’s been a while since your last one, consider getting an affordable A1C test at at Walk-In Lab – your future health may depend on it!