Introduction
Magnesium is a mineral that plays a crucial role in keeping our bodies functioning smoothly, yet it often doesn’t get the attention it deserves. Many people are unaware of just how vital magnesium is to their overall health—until they start experiencing unexplained symptoms like persistent fatigue, muscle cramps, or even irregular heartbeats. Imagine waking up each day feeling unusually tired, with no apparent reason. You’ve been eating well, exercising, and sleeping enough, but something still feels off. For many, the root cause of these issues can be traced back to an overlooked deficiency in magnesium.
Understanding your magnesium levels through a simple blood test can provide critical insights into your health. This test is particularly important for those who may be at risk of deficiency or are already experiencing symptoms that could be linked to low magnesium levels. In this blog post, we’ll explore what a magnesium blood test is, why it’s important, what it measures, and the signs and symptoms that might indicate you need one. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of why you should consider getting a magnesium blood test as part of your health routine, giving you the reassurance and control you need to manage your health effectively.

The Role of Magnesium in the Body
Magnesium is often called the “unsung hero” of minerals, quietly working behind the scenes to keep our bodies functioning properly. It’s involved in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body, making it essential for maintaining overall health. Despite its importance, magnesium is frequently overlooked in discussions about nutrition and wellness.
One of magnesium’s most critical roles is in energy production. It helps convert the food into energy, which powers everything from basic bodily functions to high-intensity workouts. Without sufficient magnesium, you might start feeling sluggish, even if you’re eating a balanced diet and getting enough rest.
Magnesium also plays a significant role in muscle function, regulating muscle contractions and helping muscles relax. This is why athletes and fitness enthusiasts often ensure they get enough magnesium—it can prevent painful muscle cramps and spasms. But even if you’re not an athlete, magnesium is essential for preventing the muscle aches and stiffness that can arise from everyday activities.
Another vital function of magnesium is its role in maintaining a steady heart rhythm. It helps regulate the heart’s electrical activity, which is crucial for preventing irregular heartbeats. This function of magnesium becomes even more important as we age since heart health can be a concern for many.
Additionally, magnesium is a key player in maintaining bone health. It works alongside calcium and vitamin D that helps keep bones strong and healthy, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. Magnesium’s role in bone health is often overshadowed by calcium, but without adequate magnesium, calcium can’t be properly absorbed or utilized by the body.
Magnesium also has a calming effect on the nervous system, helping to regulate neurotransmitters that influence mood. This is why magnesium is often recommended for those dealing with stress, anxiety, or insomnia. It’s sometimes referred to as nature’s “relaxation mineral” because of its ability to soothe and calm the mind.
Despite its numerous roles, many people don’t get enough magnesium from their diets. This can be due to poor dietary habits, the depletion of magnesium in soil and water, or certain health conditions that affect magnesium absorption. Understanding these roles highlights why it’s crucial to monitor magnesium levels and take action if they fall below the recommended range.
What Does a Magnesium Blood Test Measure?
A magnesium blood test is a straightforward procedure, yet it provides valuable insights into a crucial aspect of your health—your serum magnesium levels. But what exactly does this test measure, and why is it important?
The magnesium blood test is used to measure the level of magnesium in your blood serum, the liquid part of your blood. It’s worth noting that only a small percentage of the body’s total magnesium is actually found in the blood, with the majority being stored in bones, muscles, and soft tissues .Despite this small percentage, serum magnesium levels are a good indicator of your overall magnesium status because they reflect the amount of magnesium available for immediate use by the body.
There are different types of magnesium in the body, including serum magnesium and cellular magnesium. Serum magnesium is the most commonly tested because it’s easier to measure and provides a quick snapshot of your magnesium levels. However, it’s not a perfect reflection of the total magnesium in your body, especially the magnesium stored in your cells and bones. That said, if your serum magnesium levels are low, it’s likely that your overall magnesium stores are also depleted, making this test a useful tool in diagnosing deficiencies.
When you undergo a magnesium blood test, the results will typically show whether your magnesium levels are low, normal, or high. Normal serum magnesium levels generally range between 1.7 and 2.2 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), and this may vary slightly depending on the laboratory. If your levels fall below this range, it could indicate hypomagnesemia, or low magnesium levels, which can lead to a range of health issues. Conversely, high magnesium levels, or hypermagnesemia, though rare, can also pose health risks, particularly in individuals with kidney problems.
Understanding your test results is crucial for managing your health. If your magnesium levels are low, it could be a sign that you need to increase your intake of magnesium-rich foods or consider supplements. On the other hand, if your levels are high, it might require a different approach, such as adjusting medications or addressing underlying health conditions that could be affecting your magnesium balance.
Overall, the magnesium blood test is a simple but effective way to monitor your magnesium levels and ensure that this vital mineral is available in the right amounts to support your body’s needs. By understanding the results and taking appropriate action, you can proactively manage your health and ensure your body has the magnesium it needs to function optimally.
Purpose of the Magnesium Blood Test
The magnesium blood test serves as a critical diagnostic tool for both identifying deficiencies and guiding treatment plans. Magnesium is involved in so many bodily functions that even a slight imbalance can lead to significant health issues. Understanding the purpose of this test helps you see why it’s an essential part of maintaining good health.
Diagnostic Tool: Identifying Deficiency or Excess
One of the primary purposes of a magnesium blood test is to diagnose hypomagnesemia (low magnesium levels) or hypermagnesemia (high magnesium levels). Both conditions can lead to serious health problems if not addressed promptly.
- Hypomagnesemia: This condition can manifest in various ways, from subtle symptoms like muscle twitching and fatigue to more severe problems such as abnormal heart rhythms or seizures. If a magnesium deficiency is suspected, a blood test is the quickest way to confirm it. Once diagnosed, the deficiency can be treated through dietary changes, magnesium supplements, or addressing underlying conditions that might be causing the low levels.
- Hypermagnesemia: High magnesium levels, although less common, can be dangerous, especially for individuals with kidney disease. The kidneys are responsible for excreting excess magnesium, and if they’re not functioning properly, magnesium can build up in the body, leading to toxicity.Symptoms of hypermagnesemia can include nausea, muscle weakness, and in severe cases, cardiac arrest. A magnesium blood test can help detect this condition early, allowing for timely medical intervention.
Monitoring Health Conditions
The magnesium blood test also monitorshttps://www.walkinlab.com/products/view/magnesium-rbc-blood-test certain chronic health conditions that can affect magnesium levels. For example, individuals with diabetes, gastrointestinal disorders like Crohn’s disease, or chronic kidney disease are at a higher risk of magnesium imbalance. For these patients, regular monitoring of magnesium levels is crucial. The test helps doctors keep an eye on how well the body is managing magnesium and whether adjustments in treatment are needed.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are prone to losing magnesium through urine, particularly if blood sugar levels are not well-controlled. Monitoring magnesium levels can help manage this risk and prevent complications related to both diabetes and magnesium deficiency.
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: Conditions like Crohn’s disease or celiac disease can interfere with the body’s ability to absorb magnesium from food, leading to a deficiency. Regular testing allows for early detection and treatment.
- Kidney Disease: Since the kidneys play a key role in regulating magnesium levels, those with impaired kidney function are at risk of both deficiency and excess. Testing helps in managing these risks effectively.
Guidance for Treatment
Beyond diagnosis and monitoring, the magnesium blood test is invaluable in guiding treatment decisions. Once a deficiency or excess is identified, healthcare providers can develop a targeted treatment plan. This might include dietary recommendations, such as increasing intake of magnesium-rich foods like leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. In some cases, magnesium supplements may be prescribed.
For those with chronic conditions, the test results can inform adjustments in medication or other treatments that may be affecting magnesium levels. For example, certain diuretics used to treat high blood pressure can lead to magnesium loss, and knowing a patient’s magnesium status can help in balancing the benefits of the medication with the need to maintain adequate magnesium levels.
In essence, the magnesium blood test is not just about diagnosing a deficiency or excess; it’s about providing a roadmap for better health management. Whether you’re dealing with a chronic condition, experiencing unexplained symptoms, or simply wanting to stay on top of your health, this test offers valuable insights that can guide you and your healthcare provider in making informed decisions.
Signs and Symptoms of Low Magnesium
Low magnesium levels, or hypomagnesemia, can have a wide-ranging impact on your health, often manifesting through various physical and mental symptoms. Because magnesium is integral to so many bodily functions, even a minor deficiency can lead to noticeable issues. Here’s a breakdown of the common signs and symptoms that may suggest you’re not getting enough magnesium.
Physical Symptoms
One of the most common and telling signs of low magnesium is muscle cramps or spasms. Magnesium is essential for muscle function, helping to regulate contractions and relaxations. When magnesium is in short supply, your muscles may become tense or overactive, resulting in painful cramps, often in the legs or feet. This symptom is especially prevalent in athletes and older adults, but anyone with low magnesium can experience it.
Fatigue is another hallmark of magnesium deficiency. Magnesium plays a crucial role in energy production at the cellular level, so when levels are low, you may feel persistently tired and weak. This isn’t the kind of tiredness that goes away with a good night’s sleep—this fatigue is chronic and can affect your ability to perform daily activities.
In more severe cases, low magnesium can lead to abnormal heart rhythms, or arrhythmias. Magnesium is involved in maintaining the heart’s electrical stability, and a deficiency can disrupt this balance, leading to palpitations, irregular heartbeats, or even more serious cardiovascular issues. For individuals with preexisting heart conditions, this symptom can be particularly alarming and dangerous.
Mental and Emotional Symptoms
Magnesium’s influence extends to mental health as well. Often dubbed the “relaxation mineral,” magnesium helps regulate the nervous system and maintain a calm and stable mood. When levels are insufficient, you might experience increased anxiety, irritability, or even mood swings. Some people may feel persistently on edge or overwhelmed, without an obvious reason.
Sleep disturbances, particularly insomnia, are also linked to low magnesium levels. Magnesium helps regulate neurotransmitters and hormones that are crucial for sleep, such as melatonin. Without enough magnesium, you might find it difficult to fall asleep, stay asleep, or feel rested upon waking.
In summary, the symptoms of low magnesium can be subtle at first, but they often escalate if the deficiency isn’t addressed. Whether it’s unexplained fatigue, muscle cramps, or heightened anxiety, these symptoms are your body’s way of signaling that it needs more magnesium. If you recognize these signs in yourself, it might be time to consider a magnesium blood test to get a clearer picture of your health.

Who Should Get a Magnesium Blood Test?
A magnesium blood test isn’t just for those experiencing symptoms—it’s a valuable tool for anyone who wants to take a proactive approach to their health. However, certain groups are more likely to benefit from this test due to their higher risk of magnesium imbalance. Here’s a look at who should consider getting the test.
High-Risk Groups
Some people are more prone to magnesium deficiency due to lifestyle, health conditions, or age. These high-risk groups include:
- Individuals with Chronic Illnesses: Conditions such as diabetes, gastrointestinal disorders (like Crohn’s disease or celiac disease), and chronic kidney disease can interfere with magnesium absorption or increase magnesium loss from the body. If you have one of these conditions, regular monitoring of your magnesium levels is important to prevent deficiency.
- Older Adults: As we age, our bodies become less efficient at absorbing nutrients, including magnesium. Additionally, older adults are more likely to take medications that can interfere with magnesium levels, such as diuretics or certain heart medications. This makes them particularly susceptible to low magnesium.
- People with Poor Dietary Habits: Those who consume a diet low in magnesium-rich foods—such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains—are at a higher risk of deficiency. Processed foods, which are often stripped of their natural magnesium content, can contribute to inadequate intake.
- Athletes and Individuals with High Physical Activity: Athletes or those who engage in intense physical activity may have an increased need for magnesium due to the loss of magnesium through sweat. This makes it crucial for them to monitor their magnesium levels, especially if they experience symptoms like muscle cramps or fatigue.
When to Consider Testing
Even if you don’t fall into a high-risk category, there are specific situations where you should consider a magnesium blood test:
- Unexplained Symptoms: If you’re experiencing symptoms like persistent fatigue, muscle cramps, or irregular heartbeats, and can’t find a clear cause, a magnesium deficiency might be the culprit. A blood test can help determine whether low magnesium is behind these issues.
- Existing Health Concerns: If you have conditions that can lead to magnesium loss or interfere with its absorption, like gastrointestinal disorders, diabetes, or kidney disease, regular testing can help you manage your condition more effectively.
- During Pregnancy: Pregnant women are at a higher risk for magnesium deficiency due to increased nutritional needs. Magnesium is crucial for both maternal health and fetal development, making it a key nutrient to monitor during pregnancy.
Routine Health Check
Including a magnesium blood test in your routine health check-up can be beneficial, even if you’re not experiencing any symptoms. Since magnesium plays such a vital role in overall health, keeping an eye on your levels can help you catch potential deficiencies early before they lead to more serious health issues. This is especially important if you’re already managing other health conditions or taking medications that might affect your magnesium levels.
In summary, a magnesium blood test is a simple and effective way to ensure your magnesium levels are where they should be. Whether you belong to a high-risk group, are experiencing unexplained symptoms, or just want to take a more proactive approach to your health, this test can provide valuable insights.
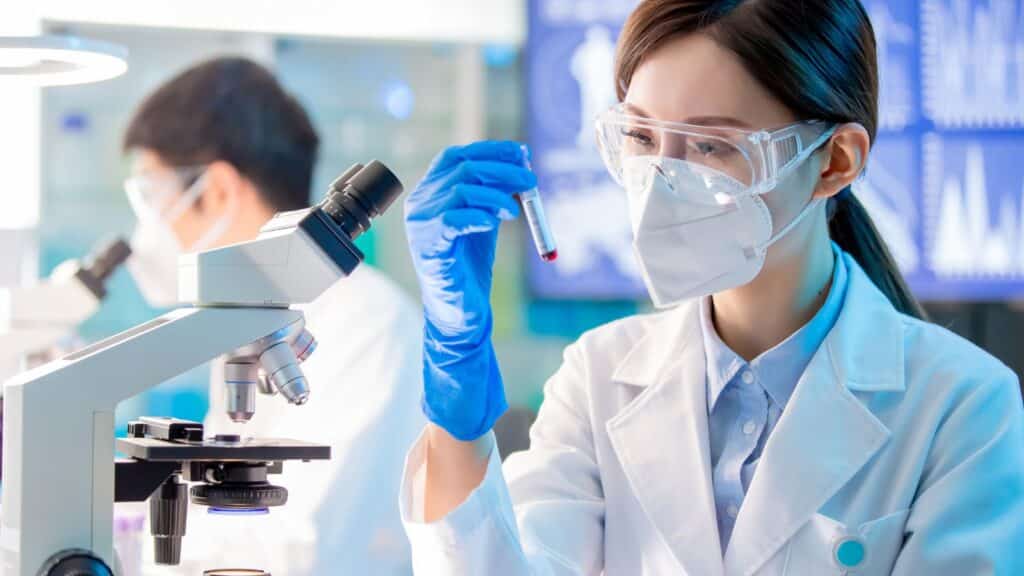

How the Magnesium Blood Test is Conducted
The magnesium blood test is a straightforward procedure that provides critical insights into your health. Understanding how the test is conducted can help ease any concerns and prepare you for the process. Here’s what you can expect before, during, and after the test.
Preparation for the Test
For most people, no special preparation is needed before a magnesium blood test. However, it’s always a good idea to inform your healthcare provider about any medications or supplements you’re taking, as certain substances can affect your magnesium levels. For instance, diuretics, antacids, and some antibiotics can alter magnesium levels, potentially skewing the results. In some cases, your doctor may advise you to avoid taking certain medications or supplements before the test to ensure accurate results.
If the magnesium test is part of a broader blood test panel, such as a complete metabolic panel, you may be asked to fast for several hours beforehand. Fasting means not eating or drinking anything other than water, typically for 8 to 12 hours before the test.
During the Test
The magnesium blood test itself is quick and relatively painless. Here’s a step-by-step overview of what happens:
- Blood Sample Collection: A healthcare professional will draw a small amount of blood, usually from a vein in your arm. You’ll be seated, and a tourniquet may be applied to your upper arm to make the veins more visible. The site is then cleaned with an antiseptic wipe to prevent infection.
- Needle Insertion: A needle is inserted into the vein, and blood is drawn into a tube attached to the needle. You might feel a brief pinch or sting, but the discomfort is minimal and lasts only a few seconds.
- Sample Handling: Once the required amount of blood is collected, the needle is removed, and a small bandage is placed over the puncture site. The blood sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
The entire blood draw process typically takes just a few minutes. Afterward, you can usually return to your normal activities immediately. If you feel lightheaded or dizzy, it’s best to sit for a few minutes and drink some water.
After the Test
Post-test, most people experience little to no side effects. It’s common to have a small bruise at the site where the needle was inserted, but this should fade within a few days. If you experience any significant pain, swelling, or signs of infection at the puncture site, contact your healthcare provider.
Results from the magnesium blood test are usually available within a few days, depending on the lab’s processing time. Your doctor will review the results and discuss them with you, explaining what your magnesium levels mean and whether any further action is needed.
- Low Magnesium Levels: If your results indicate low magnesium, your doctor may recommend dietary changes, magnesium supplements, or further tests to determine the underlying cause.
- High Magnesium Levels: If your magnesium levels are high, which is less common, your doctor will investigate potential causes, such as kidney issues or excessive supplementation, and suggest appropriate treatment.
Understanding the simplicity of the magnesium blood test process can make it easier to prioritize this important aspect of your health. Whether it’s your first time getting tested or part of routine monitoring, this test is a quick and effective way to keep your magnesium levels in check.

Conclusion: Why You Should Consider a Magnesium Blood Test
Magnesium might not be the first nutrient that comes to mind when you think about health, but its impact on your well-being is profound. From regulating muscle and nerve function to maintaining heart rhythm and supporting bone health, magnesium plays a critical role in numerous bodily functions. Yet, magnesium deficiency often goes undetected until it starts to manifest in troubling symptoms like muscle cramps, fatigue, or even irregular heartbeats.
A magnesium blood test is a simple, effective way to gain insight into your body’s magnesium levels. Whether you belong to a high-risk group, such as those with chronic illnesses, or you’re experiencing symptoms that could be related to low magnesium, this test can be a crucial step in identifying and addressing potential deficiencies. Even if you’re not currently experiencing symptoms, incorporating a magnesium blood test into your routine health check-ups can help you stay ahead of potential issues before they escalate into more serious health problems.
The test itself is quick and straightforward, with minimal preparation required. It provides valuable information that can guide your dietary choices, supplementation, and overall health management. By understanding your magnesium levels, you’re taking an important step toward ensuring your body has the support it needs to function at its best.
Where stress, poor diet, and chronic health conditions can easily lead to nutrient imbalances, getting a magnesium blood test is a proactive measure that can make a significant difference in your health. Don’t wait for symptoms to arise—take charge of your health by discussing the possibility of a magnesium blood test with your healthcare provider. It’s a small investment of time that could yield substantial benefits for your long-term well-being.
